As the world becomes more digitalised, it is no surprise how clever and innovative today’s marketers can be. Over the past decades, an increasing number of marketing strategies have surfaced to help brands and businesses further understand their audience, and learn how to effectively target them — like location-based marketing for instance.
Location-based marketing has been found to be 20 times more effective as compared to generic banner advertisements (Source: entrepreneur.com). Not only that, a 2019 report by Factual also stated that almost 9 in 10 marketers claim that location-based marketing and advertising has helped increase their sales, their customer base, and boosted their customer engagement (Source: martechadvisor.com). How? If a customer visits a mall and receives a notification from a nearby restaurant offering a discount or promotion — the chances of that customer considering to dine there will be higher simply because he/she is in the vicinity. Location-based marketing thus helps to increase the chances of your ads being both relevant and timely. With these two important factors in mind, location-based marketing thus encourages higher customer engagement and achieves better results. This, ladies and gentlemen, is the power of location-based marketing. Read on as we explore more in depth!
What is location-based marketing?
Location-based marketing uses location data which allows organisations to target their consumers on a more personalised level, especially with messaging that is relevant to the user’s physical location (Source: marketingevolution.com). Basically, the data on the user’s mobile device — specifically their current or past locations — will be used to display relevant content to them, essentially integrating the physical and digital experiences in a way (Source: groundtruth.com). The devices that we use these days are all connected to the internet and are constantly tracking our locations. This means that there is an abundance of location and spatial data available for marketing teams to identify where their consumers are, and how to effectively reach them so as to improve their brand or retail experiences. So, what are some ways marketers can use location data to serve their customers?
4 location-based marketing techniques
1. Geotargeting
Being one of the most common methods marketers use, Geotargeting determines the location of a user and sends them personalised messages based on that location (the region or its proximity to a store). One example of such an app is GrabFood. Based on the address that you key into the app, GrabFood is able to pinpoint the shops and restaurants located near you, which then eases the search process for both the user and the restaurants. Another example would be Google search results.
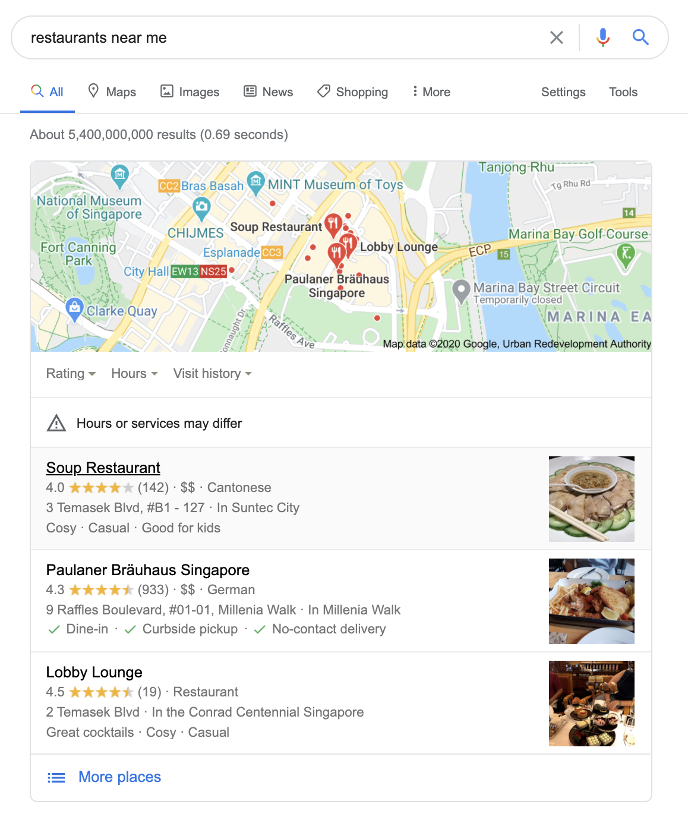
Try searching “restaurants near me”. Google will then use the location data based on the IP address of your device, and voila! Restaurants around your area will appear on the top of your search list within seconds. Thus, marketers use geotargeting to improve the customer experience by funneling information that is both personalised and relevant to the user.
2. Geofencing
Next up is Geofencing — which leverages GPS technology to demarcate a virtual radius in order to market to people within that radius. As geofencing is based on real-time data, these users within the vicinity will get to receive special deals and timely updates pushed out by the brand. This type of marketing is great for brands and marketers if they intend to capture nearby traffic and direct it to their stores. Furthermore, these users are likely to be more receptive and have a higher chance of converting given its relevance in terms of location.
Burger King made use of this method to capture McDonald’s customers in a creative way. Their Whopper Detour campaign in New York targeted customers who were either inside a McDonald’s restaurant or within 600 feet of one (Image: blog.udonis.co). Call it brilliant or sneaky, but when a customer enters one of the geofencing locations, the Burger King app sends out a coupon notification that allows customers to get a Whopper burger for just a penny (that’s $0.01 in Singapore!).
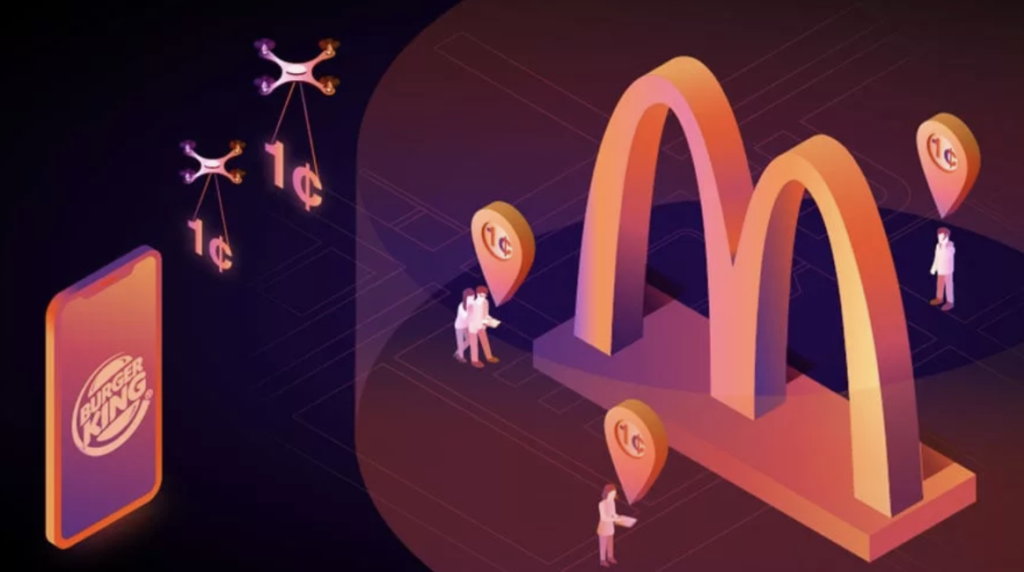

This immediately became a turning point for Burger King as the campaign saw a three times increase in Burger King’s mobile app sales during the span of their 9 days promotion, with its effects rolling over even till after the promotion had ended. What’s more impressive is that as a result of this campaign, Burger King’s app skyrocketed from No. 686 to No. 1 in both the iOS and Android app stores across all categories (Source: adweek.com).
3. Beacon marketing
Thirdly, beacon marketing — this works well for targeting existing customers within a small geographic area (Source: clevertap.com). These beacons make use of Bluetooth technology that prompts servers to send content to nearby mobile devices. Why marketers like this method is due to the simplicity of sending timely and targeted messages to people based on their physical location. Yes, users need to have their Bluetooth on in order for this to work, but this method allows marketers to communicate with their customers more directly.
313 Somerset was Singapore’s first mall that launched a beacon-based mobile advertising network.

With the help of beacon marketing, users of the Tring313 app could now get coupons and sales notifications whenever they enter the beacons’ radius (50-500 metre distance from the mall) — and it even targets travelling commuters when they stop at Somerset MRT station! The app also allowed users to shop anytime and anywhere with alerts that are catered to their personal preferences. As a result of this, the mall saw a 46% increase in sales via the app (Source: superadrianme.com).
4. Blueprints location-based marketing
Deemed as one of the more sophisticated forms of geolocation marketing, blueprints create boundaries around selected points of interest. Combined with location and consumer behavior data, marketers can fine tune the accuracy of their audience targeting to get a much better result. One brand that has managed to use this effectively is Coach.
As part of their efforts in driving in-store traffic, Coach first activated the first-to-market performance model (also known as cost per visit) that allowed marketers to pay only when legitimate in-store visits do happen. By reaching out to customers who had visited Coach stores in the past, or points of interest that identify them as a potential Coach customer, this contributed to 76% of Coach’s in-store visits, of which almost 5% of them were influenced by the ads customers saw when they were in proximity of the stores.

Lastly, Coach also made use of audience targeting tactics, whereby they extended their campaign’s reach to customers who behaved similarly to Coach’s customers based on their various location attributes and history (Source: groundtruth.com). At the start of the campaign, Coach had aimed to drive 20,000 visits; however, the brand ended it with a whopping 30,000 visits to their retail locations instead! Furthermore, by using the cost per visit performance model, 11,000 of their incremental visits did not incur any additional cost. This campaign by Coach proves just how powerful location-based marketing can be if you are able to identify, reach and influence the right audience.
Why do marketers love location-based marketing?
Simple, ROI. By targeting users in the vicinity who tend to have a higher receptivity and rate of conversion, the ROI for location-based marketing is what keeps marketers turning to this strategy. With this, they get to deliver a more targeted message to customers, which helps increase brand awareness and strengthens their relationship with them. Not only is it perceived as beneficial for brands, but this adds value to consumers too as it delivers personalised offers at the right time, making this a win-win for both parties!
What are some concerns?
A common concern of location-based marketing would be its effectiveness, especially in Singapore. Due to our small geographical and population size, location-based marketing can have varying degrees of effectiveness depending on how big/small a radius brands are looking to target, as well as what their objectives might be. If your campaign objective is to grow awareness and reach with a more generic target audience such as the masses, then location-based marketing may offer limited value here. However, if brands are looking to target more specific audiences and communities, and are looking to drive nearby traffic and conversions, then perhaps this is where location-based marketing can come in handy. So before jumping onto this strategy, carefully consider what your objectives are, and who your target audience might be.
Another common concern would be privacy. Although many users understand that details such as their location have to be revealed in order for this to work, many of them are still very skeptical and hesitant. As a result, a large number of smartphone users today have disabled their location settings. As with customer data, businesses that use location data as part of their customer-serving strategy, must use it responsibly and at the same time, implement ways to reassure their customers of it. Possible ways include letting users opt into and out of location services when using related apps, anonymising data, as well as presenting cybersecurity solutions and protocols for users. The best way though, is to be upfront about it — tell users how their data will be used and whether or not you will be sharing them with any third parties — it’s better than being ambiguous about it. If users are willing to accept these terms, then it means that they are likely to be more open to the rest of what you have to offer.
The future of location-based marketing
Today, more and more marketers are giving location-based marketing a shot, given how effective it can be. However, many are not just stopping there — they are also trying to push past boundaries and find out what the future holds next for location-based marketing. Here are a couple of up and coming trends we have identified.

Augmented location
This one of the ways in which brands can turn their location marketing game up a notch — think Pokémon GO.Pokémon GO integrates the user’s location data and turns it into a fun and interactive experience where your movement in the game as well as in the real world, gets synced up. The app also makes use of the mobile device’s camera function, which acts as an augmented reality lens for users to “capture” their Pokémon.

Mobile app localisation
Mobile apps configured in a way that feeds users with more localised content will become increasingly more mainstream. As businesses tweak their content strategies to better fit the needs of audiences in specific regions, customers and users will start to benefit from more relevant, personalised and localised experiences, enhancing the effectiveness of ads being served as well.
The ultimate goal here — is for both consumers and businesses to willingly embrace location-based marketing. The world is speeding forward, so we must have the thirst to keep jumping on new trends and trying out new things in order to keep up. As marketers, it’s high time we recognise and acknowledge that location-based marketing gives us the opportunity to reach consumers at the right time, and with the right message, helping us stay relevant in an age that never stands still.
— —
Hero image: Henry Perks, Unsplash
